special tests cluster for shoulder impingement vs. tear|special tests for shoulder impingement : distributing The current study investigated 8 different clinical tests to determine an optimal testing cluster to differentiate individuals with varying degrees of subacromial impingement secondary to rotator cuff pathology (rotator cuff . Have fun playing the amazing Crisis Core - Final Fantasy VII .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Note: This incident occurred in 2012. Manhattan prosecutors .
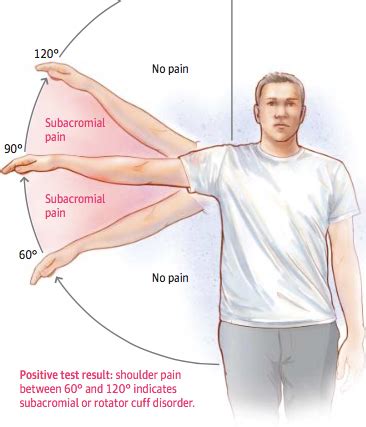
Painful arc: SN: .75 (.54–.96) SP: .67 (.52–.81) +LR: 2.25 (1.33–3.81) Testing: Shoulder is elevated in scapular plane abduction to full elevation and then lowered in same motion. Positive Test: Pain or pain from 60 to 120 degrees scapular plane abduction.Orthopaedic Special Tests may help us with symptom reproduction which can be .Based on the Park et al study, the combination of the following 3 special . The current study investigated 8 different clinical tests to determine an optimal testing cluster to differentiate individuals with varying degrees of subacromial impingement secondary to rotator cuff pathology (rotator cuff .
Among tests for infraspinatus tears, external rotation lag signs at 0° had a specificity of 98% (95% CI=96% to 100%) and a likelihood ratio of 6.06 (95% CI=1.30 to 28.33), and the .The two most commonly used tests for impingement are Neer's Sign and the Hawkins–Kennedy test 8, 9. Neer’s sign. This test allows demonstration of a pain during passive abduction of the .
The first test is the Hawkins-Kennedy test, which is said to compress the rotator cuff tendons in the subacromial space. To perform this test, bring your patient’s shoulder in 90° of forward flexion and support it on your arm by putting your . How To Test for Shoulder Impingement. After reviewing the reliability and diagnostic accuracy of certain tests for SAIS, researchers determined: 1. The Neer test is .
Based on the Park et al study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator cuff tear: The Drop-Arm Sign; The Painful Arc Sign; Infraspinatus Muscle .Definition: Shoulder impingement occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles are compressed or "impinged" between the bones of the shoulder joint, particularly under the acromion .; Symptoms: Pain when lifting the arm, especially overhead; pain that worsens at night; limited range of motion; weakness in the shoulder .; Diagnosis: Diagnosed through special .Learn this shoulder special test cluster designed by Michener et al. to check for signs of subacromial impingement and enable early diagnosis and effective treatment. Get the information you need to help your patient now.
The aim was to assess diagnostic accuracy of 15 shoulder special tests for rotator cuff tears. From 02/2011 to 12/2012, 208 participants with shoulder pain were recruited in a cohort study. . Doukas WC, Murphy KP. Reliability and diagnostic accuracy of 5 physical examination tests and combination of tests for subacromial impingement. Archives . A shoulder impingement test is one way to diagnose a shoulder injury. Your physical therapist or doctor may perform one or more type of this physical exam on your shoulder to help determine the .Primary External Impingement related to structural changes, either congenital or acquired, that mechanically narrow the subacromial space such as; bony narrowing or osteophyte formation, bony malposition after a fracture, or an increase in the volume of the subacromial soft tissues. .
The shoulder exam can be challenging in patients and confidence in your special tests skills can help improve diagnostic accuracy. . “Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement . Ha KY, Choy S, Joo MW, Chung YG. The passive compression test: a new clinical test for superior labral tears of the shoulder. Am J Sports Med. 2007 Sep;35(9 .The Fitzgerald test utilizes two different test positions to determine if the patient has an anterior or posterior labral tear. To test for an anterior labral tear, the patient lies supine, then the physical therapist (PT) performs flexion, external rotation, and full abduction of the hip, followed by extending the hip, internal rotation, and .

Note from Dr. B: Impingement syndrome is a constellation of symptoms that includes pain over the top and outer aspect of the shoulder that are typically aggravated between 45-120 degrees of shoulder flexion and abduction. As Coach E describes, the symptoms are often activity related and intermittent at the start, but over time, they can progress and become constant, even .
shoulder special tests in clinical prac-tice. For myriad reasons, it is likely that new clinicians will wish to emulate this clinical practice. Evolving the Approach to Diagnosing Shoulder Problems We argue that academic institutions and practicing clinicians should stop teach-ing and using shoulder special tests re-lated to RCRSP. Subacromial impingement is the most common cause of shoulder pain which occurs as a result of compression of the rotator cuff muscles by superior structures (AC joint, acromion, CA ligament) leading to inflammation and development of bursitis. . impingement tests (see complete physical exam of shoulder) . first line and mainstay of . This study investigated the diagnostic utility of 8 commonly used subacromial impingement tests in individuals with varying degrees of rotator cuff (RTC) pathology. The purpose of the study was to validate a cluster of tests that could be used to distinguish degrees of RTC tears in individuals with subacromial impingement syndrome.
special tests for subacromial impingement
The two most commonly used tests for impingement are Neer's Sign and the Hawkins–Kennedy test 8,9. Neer’s sign. This test allows demonstration of a pain during passive abduction of the arm with the scapula stabilized, the examiner lifting the arm in the scapular plane with the arm internally rotated . It was described originally in 1977 .
A common variation of the test is described as the patient moving the shoulder into external rotation while simultaneously moving the forearm into the supine position against resistance. It is a complex movement and the patient is encouraged to perform it without resistance first so they can elicit an effective response when resistance is added.This test is commonly used to identify possible subacromial impingement syndrome. Technique [edit . Physical examination tests of the shoulder: a systematic review with meta-analysis of individual tests. British journal of sports medicine, 42(2), 80-92. . Special Tests; Shoulder; Shoulder - Special Tests; Shoulder - Assessment and Examination;Tests for other shoulder pathologies may be (+) or (-) due to the variable clinical presentation of internal impingement. Understand that there is no proven combination of test findings that identify internal impingement. Subacromial Impingement: Test item cluster; Full/partial thickness .
Test Item Cluster: When this test is combined as a cluster with the Painful Arc Sign and the Infraspinatus test, and all three tests report a positive, then the positive likelihood ratio is 10.56 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is .17. If two of the three tests are positive, .
Special tests for shoulder impingement. The Park et al. Shoulder Impingement Testing Cluster, Hawkin's Kennedy, Infraspinatus Strength Test, Painful Arc Test, Michiner et al. Shoulder Impingement Testing Cluster, Neer's Test, Empty Can Test, Supine Impingement Test (Screening Tool). The reliability, specificity, sensitivity, validity, safety, and screening for .Test Item Cluster [edit | edit source]. When this test is combined as a cluster with the Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign and the Infraspinatus test, and all three tests report a positive, then the positive likelihood ratio is 10.56 and if all three tests are negative, the negative .The population with a combination of cam and pincer often suffer from a slipped capital femoral epiphysis called the S C F E. They show varying degrees of hip impingement. An estimated 85% of patients with FAI have this type of mixed morphology, although Raveendran et al. found only 2% of subjects in their prospective longitudinal cohort study had mixed morphology (albeit in a .The rotator cuff is a cluster of important muscles and tendons in the shoulder that serves to support the shoulder joint and enable rotation of the arm. The tendons in the rotator cuff are thick and strong. . Rotator cuff tear vs. shoulder impingement tests. Through rigorous tests, your physical therapist can help determine the cause of your .
Shoulder pathology and dysfunction represent some of the most commonly diagnosed and treated conditions by primary care, sports medicine, and orthopedic providers.[1] This comprehensive review article discusses the clinical pearls and tips and tricks for delineating complex shoulder pathologies.Biceps tendinopathy refers to inflammation or degeneration of the long head of the biceps tendon. It is an important cause of anterior shoulder pain and it is usually seen in association with other shoulder pathologies, such as rotator cuff tears and shoulder impingement. There are two specialized tests to confirm the presence of biceps .
How To Test for Shoulder Impingement. After reviewing the reliability and diagnostic accuracy of certain tests for SAIS, researchers determined: 1. The Neer test is useful to rule out SAIS. 2. The Jobe (empty can) test is useful to confirm a diagnosis of SAIS. 3. The painful arc test is useful to rule out and confirm SAIS. 4.
The Hawkins Kennedy Sign is one of the classic special tests for shoulder impingement. The examiner brings the arm up to 90 degrees and internally rotates t. There is a paucity of systemic review data and meta-analysis relating to Orthopaedic Special Tests pertaining to the shoulder. The most relevant reviews will be summarised. . the External Rotation Lag Sign and Drop Arm Test were deemed of value for cuff tears, and Supine Impingement Test was reported to possibly rule out cuff tear when .
special tests for shoulder impingement
Simple Shoulder Test . range of motion testing, strength testing and special tests. Active and passive range of motions that the clinician needs to test are: forward flexion, abduction and internal/external rotation at 0° and 90°. . To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed.
Tests with low LR− help “rule out” competing conditions thus one might choose to consider tests or clusters of tests for shoulder labrum tears, impingement, or a rotator cuff tear. As a reminder, clustering tests often leads to higher LR+ with a sacrifice of LR−, unless the cluster was mathematically designed as a screen.

WEB0:59. utokki_0 Cristiano Ronaldo having a gay feet feast after carrying the whole Al Nassr FC team. 21 224. 25. 5 months ago. MrDeepFakes has all your celebrity deepfake porn videos and fake celeb nude photos. Come check out your favorite Hollywood or Bollywood actresses, Kpop idols, YouTubers and more!
special tests cluster for shoulder impingement vs. tear|special tests for shoulder impingement